The Synthetic Immune Therapy Lab
 Current Team:, Viktor Lang (PhD candidate), Viana Wille (technician), Victoria Klepsch (PI), Dominik Humer (PhD candidate)
Current Team:, Viktor Lang (PhD candidate), Viana Wille (technician), Victoria Klepsch (PI), Dominik Humer (PhD candidate)
Research interest
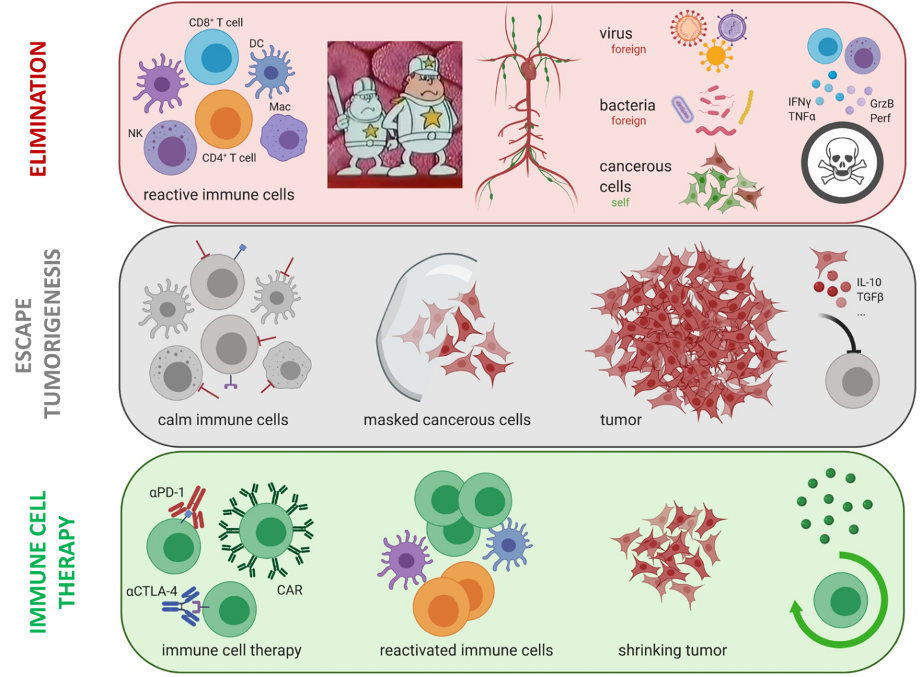
Cancer is a severe health problem with increasing prevalence. Failure of cancer immune surveillance is emerging as a crucial event in cancer aetiology. Even though PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 cell surface immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) has been a game changer for the treatment of solid cancer, a sizable subset of patients still fails to benefit. Of note, ICB resistance via upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints has increasingly been observed. Therefore, uncovering underlying molecular mechanisms that govern immune control of cancer is of highest clinical relevance. Particularly, the validation of alternative and druggable immune checkpoint candidates for improved immunotherapy is envisioned as a way forward to extend the benefits of clinical treatment to larger numbers of cancer patients in the future. There is an urgent need to explore novel immunotherapeutic avenues with the ultimate goal of strengthening the patient’s immune system for a longer progression-free survival.
Past achievements and research efforts include:
NR2F6 and its role in tumor immunology
1) NR2F6 as a novel potential immune checkpoint
The identification of the nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 as a checkpoint for cancer immune surveillance. We could show that Nr2f6-/-, and even Nr2f6 heterozygous mice spontaneously reject tumors due to increased infiltration of CD4 and CD8 positive T cells which produce more cytokines like IL2, IFNγ, and TNFα. Mechanistically we could show that NR2F6 acts as a suppressor of NFAT/AP-1 and if missing (like in the KO), more NFAT mediated cytokines can be transcribed.
Hermann-Kleiter N*, Klepsch V*, Wallner S, Siegmund K, Klepsch S, Tuzlak S, Villunger A, Kaminski S, Pfeifhofer-Obermair C, Gruber T, Wolf D, Baier G. *both authors contributed equally to this work. The Nuclear Orphan Receptor NR2F6 Is a Central Checkpoint for Cancer Immune Surveillance. Cell Rep. 2015 Sep 29; 12(12):2072-85. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.035. Epub 2015 Sep 17. IF 8.032
2) NR2F6 inhibition potentiates responses to PD-L1/PD-1 cancer immune checkpoint blockade
Building on the results from 2015, we were able to show a synergistic tumor rejection phenotype of PD-L1 blockade and missing Nr2f6 in different tumor models. Regarding human relevance of NR2F6, we could show in siRNA-mediated knock-down experiments enhanced cytokine production in human T cells, as well as an increased expression of NR2F6 in TILs of lung cancer patients, supporting the local repression of cytokine producing T cells due to NR2F6.
Klepsch V, Hermann-Kleiter N, Do-Dinh P, Jakic B, Offermann A, Efremova M, Rieder D, Krogsdam A, Perner S, Gamerith G, Sopper S, Tzankov A, Trajanoski Z, Wolf D and Baier G. Nuclear Receptor NR2F6 Inhibition Potentiates Responses to PD-L1/PD-1 Cancer Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 18;9(1):1538. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04004-2. IF 12.353
3) Targeting NR2F6 in T cells primes tumors for immune checkpoint therapy
The finding that siRNA-mediated knock-down of Nr2f6 in combination with PD-L1 blockade leads to better tumor rejection, led us to this publication, where we could show a comparable phenotype using the CRISPR/Cas9 system in murine T cells. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated loss of Nr2f6 leads to elevated cytokine production as well as better tumor rejection when a co-therapy of an ACT with PD-L1 or CTLA-4 blockade is administered to tumor-bearing mice.
Klepsch V, Pommermayr M, Humer D, Brigo, N, Hermann-Kleiter N, Baier G. Targeting the orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 in T cells primes tumors for immune checkpoint therapy. Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Jan 14;18(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0454-z. IF 5.11
NR2F6 and its role in colitis
Nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 as a safeguard against experimental murine colitis
We used our Nr2f6-deficient mice in an experimental murine colitis model (DSS induced) and observed more weight loss, more signs of inflammation in KO mice with shortened colons and a higher disease score. In several different approaches, we were able to show, that NR2F6 transactivates a mucus producing gene (Muc2). Therefore, Nr2f6-deficient mice have less mucus and are prone to intestinal inflammation.
Klepsch V, Gerner RR, Klepsch S, Olson WJ, Tilg H, Moschen AR, Baier G and Hermann-Kleiter N. Nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 as a safeguard against experimental murine colitis. Gut. 2018 Aug;67(8):1434-1444. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313466. Epub 2017 Aug 4. IF 17.016
Major Publications [R = review] and future plans
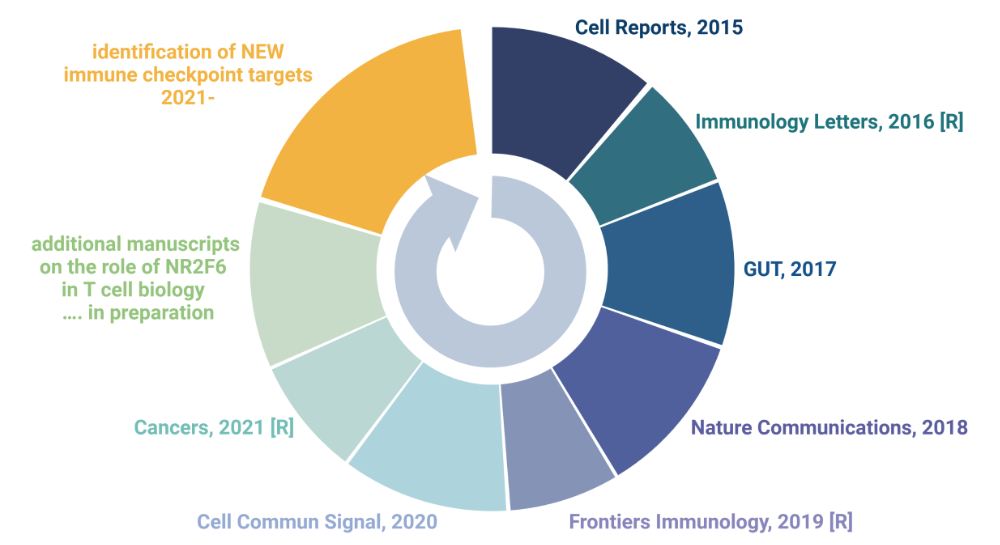
Future Perspective and long-term goal
Additionally and as a long-term approach, my lab will focus on identifying new targets and signaling pathways important in immune oncology. As we already established the CRISPR/Cas9 gene modification in mice in Innsbruck, we want to use this method to explore and identify genes essential for T cell tolerance in fighting cancerous cells using CRISPR/Cas9 screening approaches. This gene modification method can also be used to quickly test new genes on feasibility and potential as new successful targets. As many patients still not respond to immunotherapy, the prospective role of more, yet undefined genes need to be investigated.
The future of immuno-oncology drug development is positioned in combination therapies. The nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 might be a great emerging next generation target to combine established as well as novel, yet undefined receptor pathways improving T cell efficacy, increasing the percentage of cancer patients who respond to treatment.
Publication list (all peer-reviewed)
Koutník J, Klepsch V, Pommermayr M, Thuille N, Baier G, Siegmund K. A MLR-Based Approach to Analyze Regulators of T Lymphocyte Activation In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 10;23(10):5337. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105337. PMID: 35628145. IF 6.2
Klepsch V, Siegmund K, Baier G. Emerging Next-Generation Target for Cancer Immunotherapy Research: The Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR2F6. Cancers (Basel) 2021 May 26;13(11):2600. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112600. IF 6.64
Jakic B, Olson WJ, Siegmund K, Klepsch V, Kimpel J, Labi V, Zehn D, Baier G and Hermann-Kleiter N. Loss of the orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 enhances CD8+ T-cell memory via IFN-γ. Cell Death Diss. In Revision 2020. IF 6.3
Tymoszuk P, Nairz M, Brigo N, Petzer V, Heeke S, Kircher B, Hermann-Kleiter N, Klepsch V, Theurl Igor, Weiss G, Pfeifhofer-Obermair C. Iron supplementation interferes with immune therapy of murine mammary carcinoma by inhibiting anti-tumor T cell function. Frontiers. Accepted 2020. IF 4.5
Klepsch V, Pommermayr M, Humer D, Brigo, N, Hermann-Kleiter N, Baier G. Targeting the orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 in T cells primes tumors for immune checkpoint therapy. Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Jan 14;18(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0454-z. IF 5.11
Thuille N, Siegmund K, Klepsch V, Schörgenhuber J, Danklmaier S, Leitges M, Baier G. Loss-of-function phenotype of a PKCθT219A knockin mouse strain. Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Nov 6;17(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0466-8. IF 5.11
Olson WJ, Jakic B, Labi V, Schoeler K, Kind M, Klepsch V, Baier G, Hermann-Kleiter N. Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR2F6 Suppresses T Follicular Helper Cell Accumulation through Regulation of IL-21. Cell Rep. 2019 Sep 10;28(11):2878-2891.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.024. IF 7.815
Klepsch V, Moschen AR, Tilg H, Baier G, Hermann-Kleiter N. Nuclear Receptors Regulate Intestinal Inflammation in the Context of IBD. Front Immunol. 2019 May 14;10:1070. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01070. eCollection 2019. Review. IF 4.716
Klepsch V, Hermann-Kleiter N, Do-Dinh P, Jakic B, Offermann A, Efremova M, Rieder D, Krogsdam A, Perner S, Gamerith G, Sopper S, Tzankov A, Trajanoski Z, Wolf D and Baier G. Nuclear Receptor NR2F6 Inhibition Potentiates Responses to PD-L1/PD-1 Cancer Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 18;9(1):1538. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04004-2. IF 12.353
Efremova M, Rieder D, Klepsch V, Charoentong P, Finotello F, Hackl H, Hermann-Kleiter N, Löwer M, Baier G, Krogsdam A, Trajanoski Z. Targeting immune checkpoints potentiates immunoediting and changes the dynamics of tumor evolution. Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 2;9(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02424-0. IF 12.353
Gerner RR, Klepsch V, Macheiner S, Arnhard K, Adolph TE, Grander C, Wieser V, Pfister A, Moser P, Hermann-Kleiter N, Baier G, Oberacher H, Tilg H, Moschen AR. NAD metabolism fuels human and mouse intestinal inflammation. Gut. 2017 Sep 6. pii: gutjnl-2017-314241. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314241. IF 17.016
Klepsch V, Gerner RR, Klepsch S, Olson WJ, Tilg H, Moschen AR, Baier G and Hermann-Kleiter N. Nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 as a safeguard against experimental murine colitis. Gut. 2017 Aug 4. pii: gutjnl-2016-313466. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313466.. IF 17.016
Siegmund K, Klepsch V, Hermann-Kleiter N, Baier G. Proof of Principle for a T Lymphocyte Intrinsic Function of Coronin 1A. J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 14;291(42):22086-22092. IF 4.01
Pfeifhofer-Obermair C, Albrecht-Schgoer K, Peer S, Nairz M, Siegmund K, Klepsch V, Haschka D, Thuille N, Hermann-Kleiter N, Gruber T, Weiss G, Baier G. Role of PKCtheta in macrophage-mediated immune response to Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice. Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Jul 28;14(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12964-016-0137-y. IF 5.324
Moschen AR, Gerner RR, Wang J, Klepsch V, Adolph TE, Reider SJ, Hackl H, Pfister A, Schilling J, Moser PL, Kempster SL, Swidsinski A, Orth Höller D, Weiss G, Baines JF, Kaser A, Tilg H. Lipocalin 2 Protects from Inflammation and Tumorigenesis Associated with Gut Microbiota Alterations. Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Apr 13;19(4):455-69. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.03.007. IF 17.872
Klepsch V, Hermann-Kleiter and Baier G Beyond CTLA-4 and PD-1: Orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 as T cell signaling switch and emerging target in cancer immunotherapy. Immunology Letters, 2016 Mar 15. pii: S0165-2478(16)30032-3. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.03.007 IF 2.436
Hermann-Kleiter N*, Klepsch V*, Wallner S, Siegmund K, Klepsch S, Tuzlak S, Villunger A, Kaminski S, Pfeifhofer-Obermair C, Gruber T, Wolf D, Baier G. *both authors contributed equally to this work. The Nuclear Orphan Receptor NR2F6 Is a Central Checkpoint for Cancer Immune Surveillance. Cell Rep. 2015 Sep 29; 12(12):2072-85. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.035. Epub 2015 Sep 17. IF 8.032
Schuler F, Baumgartner F, Klepsch V, Chamson M, Müller-Holzner E, Watson CJ, Oh S, Hennighausen L, Tymoszuk P, DopplerW, Villunger A. The BH3-only protein BIM contributes to late-stage involution in the mouse mammary gland. Cell Death Differ. 2015 Jun 5; doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.61 IF 8.184
Baumgartner F, Wöss C, Pedit V, Tzankov A, Labi V, Villunger A. Minor cell death defects but reduced tumor latency in mice lacking the BH3-only proteins Bad and Bmf.
Oncogene. 2013 Jan 31; 32(5): 621–630. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012. IF 7.97